General Domain and AD Notes
Windows Active Directory Domain Trust:
Understanding Trust :
Trust relationships enable access to resources can be either one-way or two-way.
- A one-way trust is a unidirectional authentication path created between two domains.
- In a one-way trust between Domain A and Domain B, users in Domain A can access resources in Domain B. However, users in Domain B can't access resources in Domain A.
- Some one-way trusts can be either non-transitive or transitive depending on the type of trust being created.
- In a two-way trust, Domain A trusts Domain B and Domain B trusts Domain A. This configuration means that authentication requests can be passed between the two domains in both directions. Some two-way relationships can be non-transitive or transitive depending on the type of trust being created.
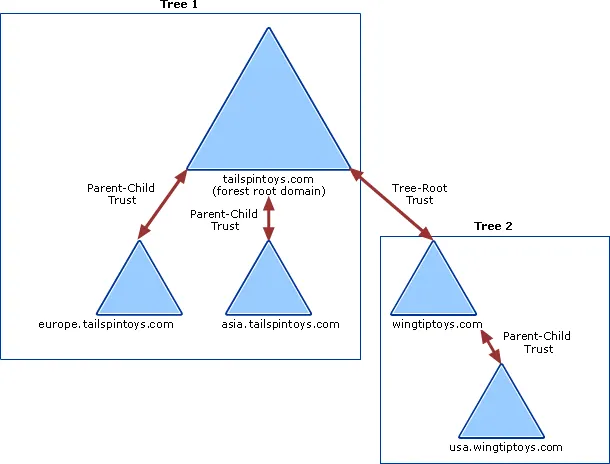
- All domain trusts in an on-premises AD DS forest are two-way, transitive (able to take a direct object) trusts
- When a new child domain is created, a two-way, transitive trust is automatically created between the new child domain and the parent domain.
Base Network Info
- DNS - Critical for AD DS functionality; DCs typically run DNS
- DHCP - Often configured alongside DCs for IP management
- Network Policy Server - RADIUS/network access control
AD Services (more documentation on prev. page)
- Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) - Core DC functionality for authentication, authorization, and directory services
- AD Federation Services (AD FS) - Single sign-on and federated identity
- AD Certificate Services (AD CS) - PKI infrastructure for certificates
- Windows LAPS - Local admin password management across domain
Management Tools:
- Windows Admin Center - Web-based management interface
- Azure Arc - Hybrid cloud management
- WSUS - Update management for domain computers
ACTIVE DIRECTORY SPECIFICS
Microsoft AD Documentation - more info